Paraphrasing is a skill that is often assessed in exams. Experienced teacher and assessment writer Judy Alden examines how to teach it, offering practical tips and techniques you can take straight to the classroom.
Introduction
As English Language teachers, one of our core aims is to teach our learners how to express themselves. And I’m sure, like myself, you receive a great deal of satisfaction when your learners are able to reproduce the language that you’ve taught them. But what else can we do to avoid learners simply sticking to the script? The answer is quite simple: we need to demonstrate the power of paraphrasing in the classroom.
Paraphrasing is an essential skill that helps learners develop their communicative ability beyond their existing knowledge of language. In other words, it’s an empowering skill that enables learners to keep learning new words or phrases similar to the ones they already know. This is why in this article we’re going to look at a paraphrasing technique, activities to encourages students to paraphrase, and how paraphrasing is often a skill that is assessed in exams in all the subskills.
Synonyms for all levels
Teaching synonyms is a straightforward technique that can be adapted to all levels of learners. In fact, it’s probably one of the first strategies used with lower level learners to start expanding their vocabulary. For example, when teaching the A2 word ‘grandmother’ the synonyms ‘grandma, granny, gran, nanna, nan’ can also be taught since they are the informal versions of ‘grandmother’ which native speakers would tend to use. With higher level students, you can use the same approach but with a more complex word bank of synonyms. Learners at all levels need to identify and separate which synonyms are formal (green) and which are informal (blue).

Rather than teaching students how to express something with one word, think about having them build up sets of synonyms. Then learners will know how to create their own word banks of linking words that have similar meanings so they can express themselves in a variety of ways right from the start.
Four paraphrasing activities
As every teacher knows, having a toolkit of ideas keeps things fresh in the classroom. So how can we encourage our students to use paraphrasing strategies in the classroom on an ongoing basis? One way to achieve this is to include learner-centred ice-breakers to target this skill. Here are four ice-breakers that you might want to try or adapt for your learners.
Social Butterfly (speaking)
This ice-breaker focuses on paraphrasing when answering questions at an imaginary party. Elicit a few questions from your learners and write down a list of question prompts they need to ask people (e.g. …name? …age? …hobbies? …free time? …last holiday? etc). Then tell learners that they must go and mingle. Encourage them to be ’social butterflies’ and speak to as many people as possible in the allotted time (five minutes). When they mingle, they must take turns asking and answering the questions. Let learners know that whenever someone answers a question, they must say either ‘Pardon?’ or ‘Sorry?’ to prompt their partner to rephrase what they have said.
You might want to write one or two examples up on the board. For example,
What’s your name?
My name’s Kasia.
Pardon?
I’m called Kasia.
What do you like doing in your free time?
I usually go swimming or visit my friends.
Sorry?
I like going for a swim or hanging out with my mates.
To create a party-like environment, you could play music while learners complete the task. While the activity is taking place, monitor and record good examples of paraphrasing, then go over them as a whole group.
Full Picture (reading & speaking)
To avoid having this jigsaw reading task become a detailed reading task, text selection is essential for this five-minute ice-breaker. Choose a brief, three-paragraph text that has a clear beginning, middle and end – a text about a sequence of events, for example, works well for this type of task. Then place learners into groups of three and give each student a different paragraph. If possible, put each paragraph on different colour card. Give the class one minute to read their paragraphs without writing down any notes. When time’s up, they must place their texts face down. For the next three minutes, each teammate has about a minute to tell their team what their paragraph said, so they can decide on the order of the paragraphs. For the final minute, ask teams to give reasons for their decisions. This will encourage learners to further paraphrase their texts before you, finally, ask teams to turn the texts over and check if they figured out the correct order.
Back to the Board (listening & speaking)
Back to the Board is an ice-breaker that can be adapted for all ages and levels and is an excellent student-centred approach to revising vocabulary by paraphrasing key words. To set this task up, you need to divide the class into two teams and place two chairs at the front of the class facing away from the whiteboard or Smartboard. You’ll also need a list of vocabulary learnt in previous sessions and a scoreboard. Nominate one person from each team to sit with their backs to the board. Once they are seated, emphasise that they mustn’t peek! Then, write one word from your list on the board. Ask the class to describe the word on the board. The first person with their backs to the board to shout out the correct word earns a point for their team. Have a new pair come up, and keep repeating the process until you complete the list of words. The team with the most points wins.
It’s always a good idea to demonstrate at least one example before nominating the first two students:
- Write the word on the whiteboard: e.g., houseboat
- Demonstrate an explanation without saying ‘house’ or ‘boat’: It’s an unusual type of home that floats. You can see this kind of home on canals or lakes.
Message Trail (writing)
A very quick writing task to encourage learners to paraphrase when they write is called Message Trail. This ice-breaker is easy to prepare – all you need are four sentences targeting vocabulary and structures previously learnt in class. Put learners into groups of four and give each person a piece of paper that has a different sentence. Tell learners they need to change one word in the message so that it still has the same meaning then pass the message to the person on their left. Keep passing and rephrasing the messages until the teams run out of ideas of how to paraphrase the sentences. Finally, have each team read out their final sentence to compare the types of paraphrases they came up with. The team with the most paraphrases that still reflects the meaning of the first sentence wins.
It’s also a good idea to do one example with the class. For example:
I rarely have enough time to clean my room.
I hardly ever have enough time to clean my room.
I hardly ever have enough time to clean my bedroom.
I hardly ever have time to clean my bedroom.
Only on rare occasions do I have time to clean my bedroom.
Only on rare occasions do I have time to tidy up my bedroom.
Paraphrasing for exam success
You’ll be doing your learners a great service by reinforcing how to paraphrase in the classroom, as it is a skill that is needed for exams from A2 onwards. For speaking assessments, for example, encouraging learners to paraphrase by rephrasing statements, questions or ideas, and saying them in a different way, results in higher marks.
Many listening and reading exams often have questions that test listening or reading for detailed meaning, gist, feelings, attitudes and opinions, all of which require learners to decode paraphrases. In order to achieve this, learners need to piece together the different paraphrases they hear or read in order to arrive at the correct answer. So even at the lower end of the CEFR scale, paraphrasing comes into play.
Writing exams generally award lower marks if learners simply lift vocabulary off the question paper rather than paraphrase the information provided to complete the task. For example, the new B1 Preliminary Part 1 Writing task requires learners to write an email in about 100 words using four note prompts in a situational email. Learners should always aim to rephrase the prompts and the language that appears in the email in order to receive higher marks. Importantly, they need to identify what type of information they need to write about, rephrase information in the email and add their own ideas.
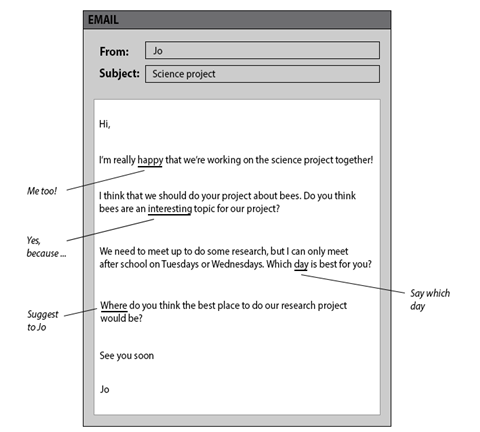
For example, learners should avoid copying large segments of text that appear in the email like this:
Hi Jo
I’m really happy we’re working on the science project together too!
Encourage them to paraphrase like this:
Hi Jo
I’m so glad we’re going to be partners for the science project!
Hopefully, by developing your learners’ ability to paraphrase in the classroom, they’ll have the skill and confidence to perform well in exams. However, the real icing on the cake is for learners to become self-aware of the power of paraphrasing and how it can support their language learning journey.
About the author

Judy Alden originally comes from Vancouver and has over 18 years’ experience teaching in South East Asia and Europe. She combines being a freelance assessment writer with delivering teacher training workshops, while also writing ELT course books and materials for international publishers.
As an assessment writer based in the UK, she often gets asked to produce listening assessments varying between British and American English. Judy has also written young learner assessment materials for the United Arab Emirates Ministry of Education.
Advancing Learning
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
 Currently reading
Currently readingAdvancing Learning: Empowering students with paraphrasing strategies
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22

























No comments yet